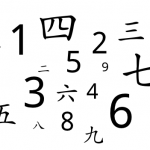Articles in the ‘Intermediate’ category Page 34
-
What’s your next step to master Chinese?
Procrastination is a major problem facing anyone trying to learn Chinese outside class (which should include almost everyone because if you only do what you’re required to do in class, you won’t get very far). In this article, I share some ideas on how I handle big projects and intimidating tasks. The gist is that you need to break things down and you need to know what your next action is.
Read → -
5 websites to help answer your questions about Chinese
It’s not always easy to know where to go when you fail to find answers to your Chinese-related questions. This article gives some advice on how to ask for help online and also introduces five websites that offer help in various forms for free.
Read → -
Reading aloud in Chinese is really hard
Reading unfamiliar Chinese text aloud is very hard. This article sheds some light on why this is the case and what consequences it has for people who learn Chinese as a second language. In general, as a student, don’t feel down if you can’t read aloud well, because it really is very hard, and as a (native speaking) teacher, please understand that reading aloud in Chinese is much harder than you think.
Read → -
Phonetic components, part 2: Hacking Chinese characters
This is the second and final article about using phonetic components to hack Chinese characters and make it considerably easier to handle similarly looking characters. This article describes both the principles and gives plenty of examples that might resolve some of your current problems for you.
Read → -
Phonetic components, part 1: The key to 80% of all Chinese characters
At least 80% of all Chinese characters are made up of one semantic component (meaning) and one phonetic component (pronunciation). The sheer number of characters formed this way means that these characters ought to be taught properly, yet I think this topic is largely glossed over. This is the first article of two dealing with phonetic components and how they can help you learn Chinese better.
Read → -
Why manually adding and editing flashcards is good for you
Creating your own flashcard is not a waste of time, even if you can find the deck you want on the internet. I have created a fair number of public decks and wouldn’t have downloaded those decks even if they would have been available at the time. Creating your own flashcards gives you control over your deck and facilitates learning in many other ways.
Read → -
Why you need goals to learn Chinese efficiently
Learning without goals might seem like a reasonable choice at first, but after a closer look, it isn’t such a good idea. First, it’s hard to imagine not having any goal at all, so setting goals is more about making your implicit goals explicit. Second, focusing only on having fun will lead to some very unusual learning strategies.
Read → -
Do you really know how to count in Chinese?
Counting in a foreign language is one of the first things we learn, yet it takes very long to master numbers in Chinese. Most students abandon practising numbers too early, leading to a surprising and serious gap in our knowledge: we simply don’t know the numbers as well as we think we do, which will cause problems both in real life and in listening comprehension tests. Do you really know how to count in Chinese? Tests included!
Read → -
5 insights from the first year of a master’s program in Taiwan
Pursuing an academic degree taught in Chinese is a great example of instrumental motivation. This article contains five insights from my first year at the Graduate Institute for Teaching Chinese as a Second Language (華語文教學研究所) in Taipei, Taiwan. Among other things, the article is about grammar, native speakers, the importance of having fun and the essence of communicative learning.
Read → -
How to get good grades when studying Chinese
Ideally, we would study Chinese just because we want to and in any manner we see fit, but this isn’t how it works for most students. Instead, we need to care about tests and grades, an extra layer added on top of our own personal goals and ambitions. This article is about studying Chinese when those tests and grades really matter, a kind of basic survival guide for both exams and courses.
Read →