Articles in the ‘Distinctively Chinese’ category Page 11
-
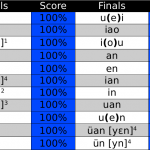
Focus on initials and finals, not Pinyin spelling
Instead of worrying too much about Pinyin spelling and what sounds each letter represents, students of Mandarin should zoom out a bit and focus on initials and finals as whole units. There are only around 60 of them and focusing on them will pay off handsomely.
Read → -
Why you should think of characters in terms of functional components
Learning about the structure of Chinese characters can help enormously when learning the language. This article is an in-depth look at functional components, i.e. parts of characters that give the whole character either its meaning or its sound. It’s also a discussion about why we really shouldn’t talk so much about radicals when learning Chinese.
Read → -
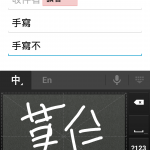
Learning to write Chinese characters through communication
How much of your character learning is done through communication? It should be a significant part, but I think this is very rare, both inside and outside classrooms. This article is about using communication to make character writing more fun, meaningful and effective.
Read → -
7 ways of learning to write Chinese characters
There are many ways of practising writing Chinese characters and they all have their pros and cons. In this article, I discuss seven different ways of practising and what advantages and disadvantages they have for you as a learner. Which do you use?
Read → -
How to Approach Chinese Grammar
In this article John Pasden discusses how to approach Chinese grammar as a foreigner, starting by debunking a few myths and then going on to how to actually learn grammar. Chinese is a language where you can very far with just a few basic concepts and patterns, so make the most of what you learn and try to use it immediately. Then extend your knowledge gradually and return to old patterns for a more detailed look later when you actually need to. Grammar learning should be driven by an actual need for better ways of expressing yourself or understanding what people say to you!
Read → -
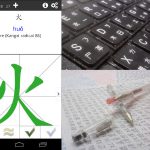
Handwriting Chinese characters: The minimum requirements
This is a guide to handwriting Chinese characters. It’s not about writing beautifully, but writing correctly, including things like stroke placement, length and direction. There are numerous examples of handwritten characters (real examples, not typed characters) along with practical exercises to see if you have grasped the core ideas. The article goes somewhat beyond the bare minimum for beginners, but is certainly a must for anyone who cares about handwriting Chinese characters.
Read → -
Learn to read Chinese… with ease?
Can you learn to read Chinese with ease? ShaoLan, among others, claims that you can. However, these arguments involve a lot of cherry-picking and are mostly exaggerated.
Read → -
Sensible Chinese character learning revisited
In a way, learning Chinese characters is very much like learning vocabulary in any foreign language and much of the efficient methods developed there works well for Chinese as well. However, characters are also fundamentally different from words in English and this influences how we should learn them as well. This article is a recap of how to learn Chinese characters in a sensible way. It is also a prologue for the upcoming character learning challenge.
Read → -
Asking the experts: How to learn Chinese grammar
How should we learn Chinese grammar? This article collects the best answers from more than 15 experts and experienced learners.
Read → -
Focusing on tone pairs to improve your Mandarin pronunciation
When learning to pronounce tones in Chinese, it makes sense to focus on words rather than single syllables. Most words in Mandarin are disyllabic and since practising these will also include tone changes (sandhi), focusing on tone pairs is recommended. This article gives you all HSK and TOCFL words, sorted by tone! First all [first tone] + [first tone], then all [first tone] + [second tone] and so on. This is great for students who need words to practise difficult combinations, but it’s also useful for teachers.
Read →